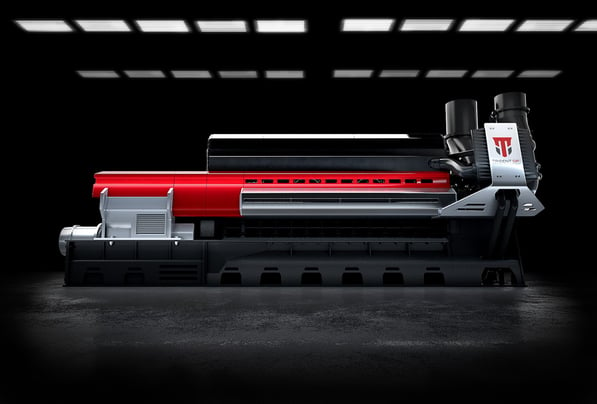
Fairbanks Morse has a rich history of innovation and possesses a wide array of manufactured products – ranging from windmills and washing machines to opposed piston (OP) engines and original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. With each passing year, there comes the demand for power in different forms. The one constant is that Fairbanks Morse is here to deliver. For over 125 years, we have been dedicated to producing quality products and solutions and look forward to doing so for many years to come.
Please enjoy the following journey of photographs to take you through how Fairbanks Morse has adapted to meet the needs of its consumers.

1889: Eclipse Wind Engine Works

The Eclipse Co. merged with E. & T. Fairbanks Morse Company and began producing scales. The company also produced and sold pumps and windmills.

1870s: Charles Morse became a partner and The Fairbanks Morse Company was created. FM began developing gasoline engines.
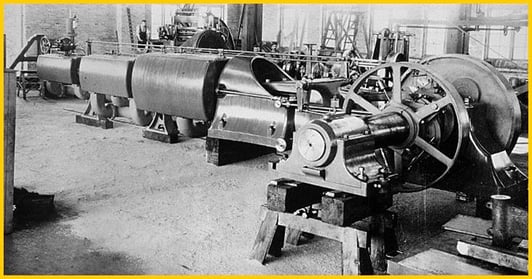
This triple-expansion engine was sold to the Chicago Arc & Light Company in 1890.
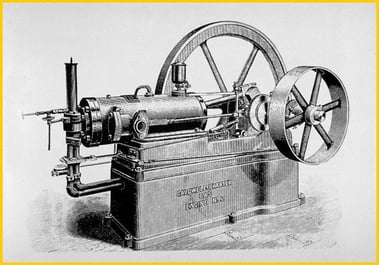
1893: The Fairbanks Morse Charter engine became our first commercially successful gasoline engine.
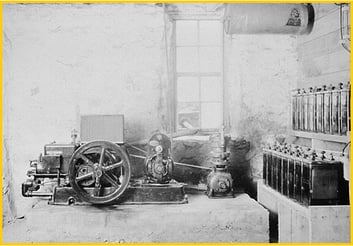
Early 1900’s: Factories and cities had electricity and running water, but rural areas did not. Fairbanks Morse worked to help by producing these home electric plants.

Electric Water Well Pumps were available.
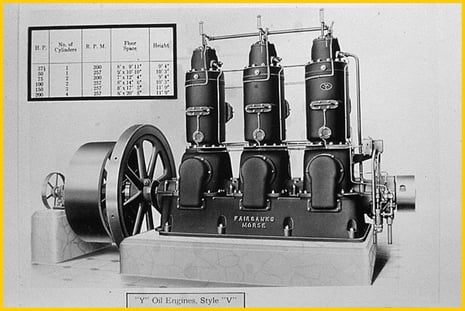
The YLA engine was our first true diesel engine. This answered our nation’s call for electricity and ship power and was well suited for marine propulsion.
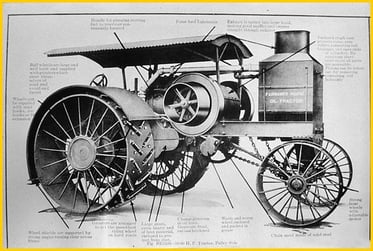
When farming became more mechanical and the amount of land in need of work continued to grow, Fairbanks answered the call by producing tractors.
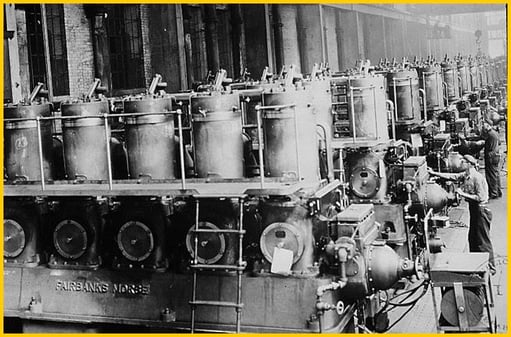
Larger diesel engines from Fairbanks Morse produced electricity in communities and powered ocean-going freighters.

In the 1920’s and 1930’s, there were dealer stores in major cities across the country that had our products, such as pumps, generators, water softeners, and the standard scale.
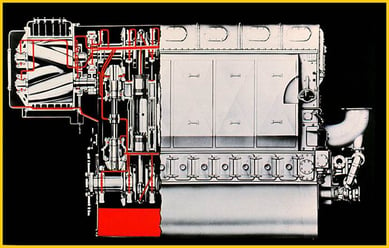
1938: The opposed piston engine was developed. Based on the engine’s size, design, and horsepower, it was built suited to power submarines and locomotives.

Fairbanks Morse, Beloit Facility during WWII. Nearly 2,300 engines were manufactured for U.S. Navy submarines and surface ships at a rate of 1 per day.

We trained hundreds of Navy sailors to operate the engines.


During the post-war period, there was a new demand to ship goods to markets. To meet this need, Fairbanks Morse built OP-powered diesel locomotives. In the late 1950’s, the production of the 24000 hp Trainmaster marked the peak of business.



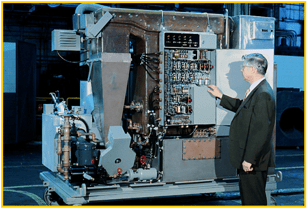
We developed products for the marine shipping industry such as desalination units and vacuum sewage treatment systems.

1960’s: The nuclear power industry was growing. Consequently, Fairbanks Morse developed and marketed emergency standby diesel generators. These were capable of starting, building to full power, and going online in less than 10 seconds. The reliable OP continued to grow in horsepower and fuel efficiency.
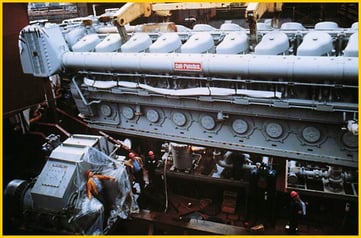
1973: We signed a licensing agreement with S.E.M.T. to manufacture and sell their Pielstick engines in the United States.
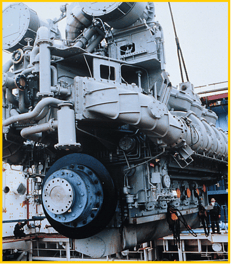
1981: FM Manufactured the largest engine built in the United States, the Colt-Pielstick PC4.2 engine.

1993: We acquired the ALCO engine product line. This engine has been used in marine and stationary applications.
2017: We unveiled the revolutionary Trident OP® at a PowerGen conference. This launch was paired with the presentation of our PoweReliability-as-a-Service™ platform.

Overall, we have come a long way from our little windmill factory to our 800,000 square-foot facility that employs over 550 people.
For over 100 years, Fairbanks Morse has been dedicated to producing quality products for our nation. Our advances in engine technology will insure that our customers receive the most modern, fuel efficient, environmentally friendly, high horsepower engines available worldwide.



